LLM - Tool Use
工具使用
大模型像是一个只能打字与我们沟通的网友,虽然这样也很有用,但我们希望大模型可以真实的帮我们做更多的事情
🌰
聚焦到编程场景,我们不想把文件内容粘贴到网页聊天框中,然后把 LLM 的输出粘贴回来
而是希望只提供一个文件路径,模型就可以
- 自动读取文件,分析其中的 bug
- read file
- 自动修改文件内容,解决 bug
- write file
- 自动运行单测/自动化测试,回归测试
- exec command
- use browser
- 自动提交代码
- exec command
- ...
总的说,需要模型跳出网页,连接到操作系统
跳出网页很简单,所有模型都提供 API 形式的调用,那如何连接到操作系统呢?
更具体的说,如何使用工具呢?
Cline 工具调用
直接看 Cline 的实现
// 调用栈
handleSendMessage
new Cline
this.startTask
this.initiateTaskLoop
this.recursivelyMakeClineRequests
this.attemptApiRequest
- mcpHub connect
// 指定工具调用格式 <read_file> <path>/xx.txt</path> </read_file>
- SYSTEM_PROMPT
- this.api.createMessage // send llm api
parseAssistantMessage // 解析 llm 输出 - 简单的语法解析
this.presentAssistantMessage
- 检查工具使用 tool_use
- write_to_file
- replace_in_file
- read_file: extractTextFromFile // nodejs fs.readFile
- list_files
- search_files
- use_mcp_tool
- execute_command
- 回传消息给 llm拼接提示词
输入框点击发送
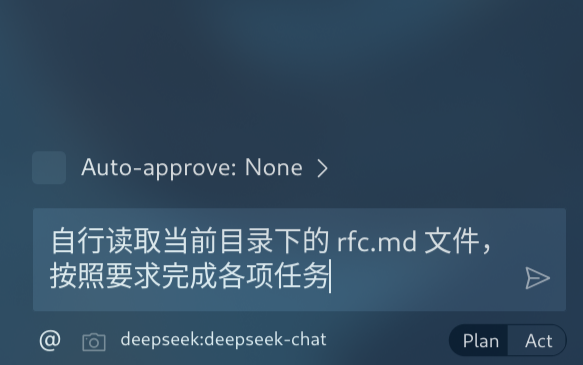
拼接编辑器和环境信息(通过 VSCode 插件 API 获得)
<task>
自行读取当前目录下的 rfc.md 文件,按照要求完成各项任务
</task>
<environment_details>
# VSCode Visible Files
lua/avante/suggestion.lua
# VSCode Open Tabs
lua/avante/suggestion.lua
# Current Time
3/5/2025, 11:08:18 PM (Asia/Shanghai, UTC+8:00)
# Current Working Directory (/home/avante.nvim) Files
${git ls-files}
</environment_details>拼接系统消息,其中明确了各工具的调用规则,当模型需要使用工具时,应该按照相应格式输出
## read_file
Description: Request to read the contents of a file at the specified path. Use this when you need to examine the contents of an existing file you do not know the contents of, for example to analyze code, review text files, or extract information from configuration files. Automatically extracts raw text from PDF and DOCX files. May not be suitable for other types of binary files, as it returns the raw content as a string.
Parameters:
- path: (required) The path of the file to read (relative to the current working directory ${cwd.toPosix()})
Usage:
<read_file>
<path>File path here</path>
</read_file>解析响应文本
将拼接后的消息发送给 LLM 后,接受并解析响应消息,检查响应消息中是否存在工具调用内容

if (llm_stream_message.endsWith('<read_file>)) {
currentToolUse = {
type: "tool_use",
name: 'read_file',
params: {}
}
}检查解析完成的响应消息,如果发现工具调用,则使用相关 API 进行处理
if (type === 'tool_use') {
switch (name) {
case "read_file":
// nodejs 读取文件
await fs.readFile(params.path, "utf8")
break
case "write_to_file":
case "replace_in_file":
case "list_files":
case "search_files":
case "use_mcp_tool":
case "execute_command":
}
}如果是工具调用,直接将读取后的结果回传给 LLM,重复此过程,直到没有工具调用或 LLM 主动向用户提出问题(也是一个工具)时停止,等待用户的输入
总结
我们要做的事情,比想象中的要简单(写一个 React/Vue)
主要就是几点
- 提示词中明确工具的使用规则、输出格式
- 解析 LLM 输出文本,提取工具信息
- 使用编程语言调用相应工具
与其说我们做的事情简单,不如说我们能做的事情很少,整个流程强依赖模型自身的能力
- 能否理解提示词中工具的使用介绍,正确的选择工具
- 能否正确的输出工具格式,和准确的参数信息
最简提示词
以目前模型的能力,这些提示词就可以开始工作
# Tools Use
## read_file
Parameters:
- path: (required) The path of the file to read (relative to the current working directory ${cwd.toPosix()})
Usage:
<read_file>
<path>File path here</path>
</read_file>
<task>
帮我读取当前目录下的 rfc.md 文件
</task>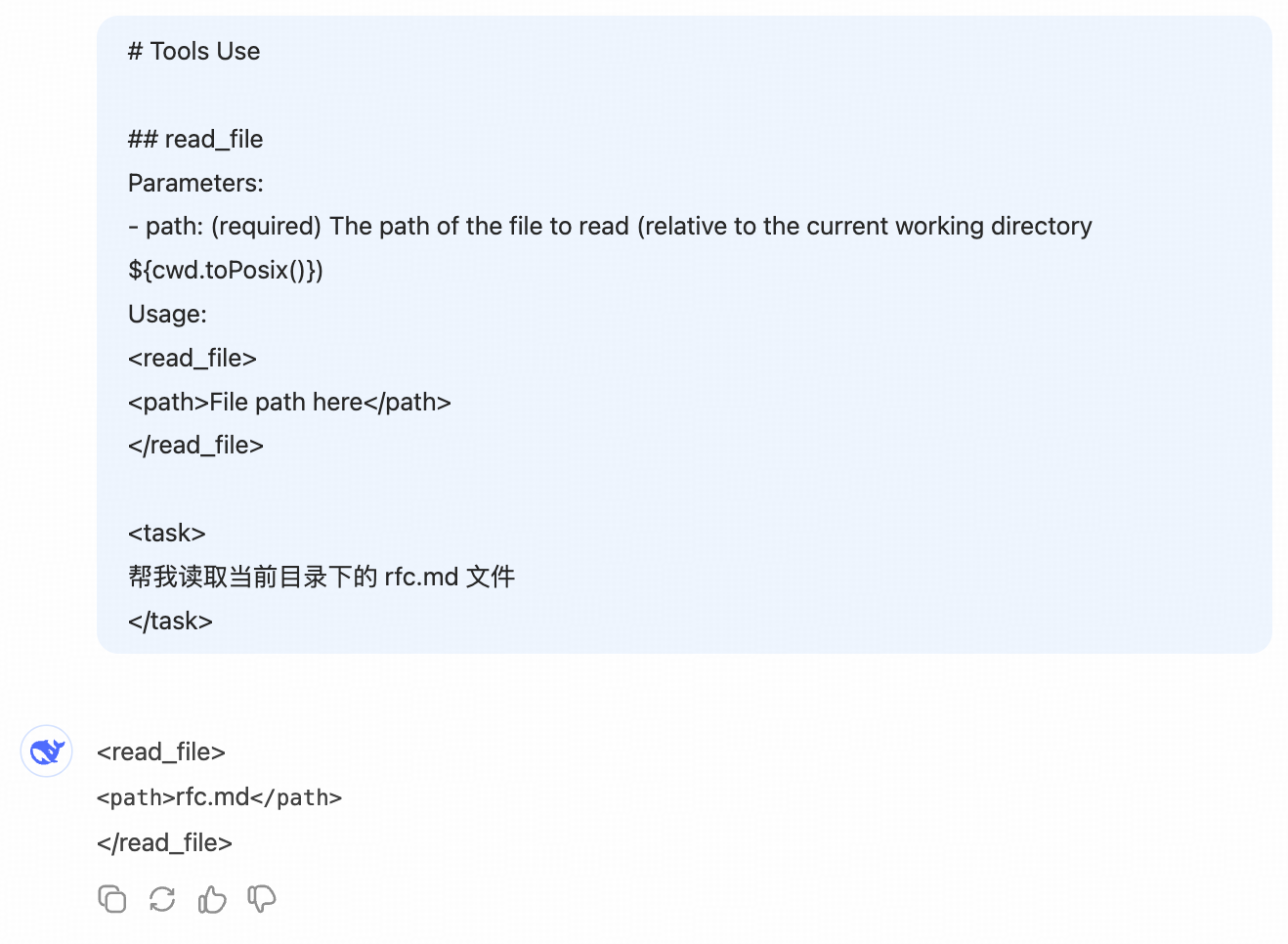
Function Call
工具调用的重要性不言而喻,所以主流模型都会进行专门的微调,来提升模型的工具使用能力
以 claude function-call 为例,我们可以在调用 API 时,传入工具列表的定义
- 输入:省了自己拼接提示词,模型 API 内部统一输入 LLM 的提示词格式
import anthropic
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219",
max_tokens=1024,
tools=[
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA",
}
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
],
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in San Francisco?"}],
)
print(response)JSON Output
更进一步,还可以接着微调模型,让其直接以 JSON 格式输出
- 输出:省了自己解析文本提取工具信息
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "<thinking>To answer this question, I will: 1. Use the get_weather tool to get the current weather in San Francisco. 2. Use the get_time tool to get the current time in the America/Los_Angeles timezone, which covers San Francisco, CA.</thinking>"
},
{
"type": "tool_use",
"id": "toolu_01A09q90qw90lq917835lq9",
"name": "get_weather",
"input": {"location": "San Francisco, CA"}
}
]
}现在直接遍历 content,判断 type: tool_use 调用代码逻辑即可
模型能力的提升,已经让我们无事可做了...
MCP 工具调用
考虑个场景,如果想新增工具呢?
- 对于 Cline 这个开源项目,可以提 issue,也可以 fork 自己改
- 但对于 Cursor 这种闭源的工具,也许只能发个反馈邮件然后等新版本发布
MCP 的出现解决了这个问题
- Model Context Protocol:模型上下文协议
MCP 是一个开放协议,用于标准化应用程序向大语言模型提供上下文的方式
- 像 Cursor/Cline 类的客户端(Client),按照规范接入 MCP 能力
- 就像是 vscode 提供了插件市场的能力
- 使用客户端的人,按照规范开发 MCP 服务器(Server)
- 也可以下载其他人的、使用远程服务
- 就像是开发/下载了插件
- 客户端通过配置文件感知所有的 MCP Server,并通过 API(HTTP)与其进行交互
- 加载/安装/使用插件
优点:
- 扩展性:可以自己定义、调用工具,而不用修改客户端(Cursor/Cline)的代码
- 开放性:MCP 市场,使用其他人开发好的 MCP 工具
- 安全性:把隐私信息放在本地服务的代码中,确保安全性
MCP 运行流程
show me the code
开发 MCP Server
通过官方提供的 SDK,开发工具服务
- 就像是学习 nodejs 时,用 koa 搭建了一个本地服务,并暴露几个接口
- 区别在于 SDK 内部封装了细节,你只需要按照签名定义函数即可
import { McpServer } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js"
const server = new McpServer({ name: "weather", version: "1.0.0", });
// Register tools
server.tool(
// 工具名称
"read_file",
// 工具说明
"Get file content",
// 工具参数
{
path: z.string().describe("file path"),
},
// 工具被调用时具体的处理逻辑
async ({ path }) => {
const content = await fs.readFile(path, "utf8");
return {
content: [
{
type: "text",
text: alertsText,
},
],
};
},
);
// 启动服务,localhost:12345
await server.connect()客户端配置
在客户端的配置文件中,列出所有的 MCP Server 和启动方式
- 比如 cursor 的配置地址:
~/.cursor/mcp.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["$MCP_PATH/fs/dist/index.js"]
}
}
}客户端进行服务发现、注册
客户端(Cursor/Cline/ Claude Desktop...)启动/运行时,就可以根据配置文件启动所有 Server,
- 通过 API 与所有服务通信,获取每个服务中工具的名称、说明、参数信息
- 与 LLM 对话时,将工具信息提供给 LLM(function-call / 提示词拼接)
- 发现 LLM 输出中需要调用工具时,通过 API 请求对应 MCP Server,将 MCP 的处理结果发送给 LLM
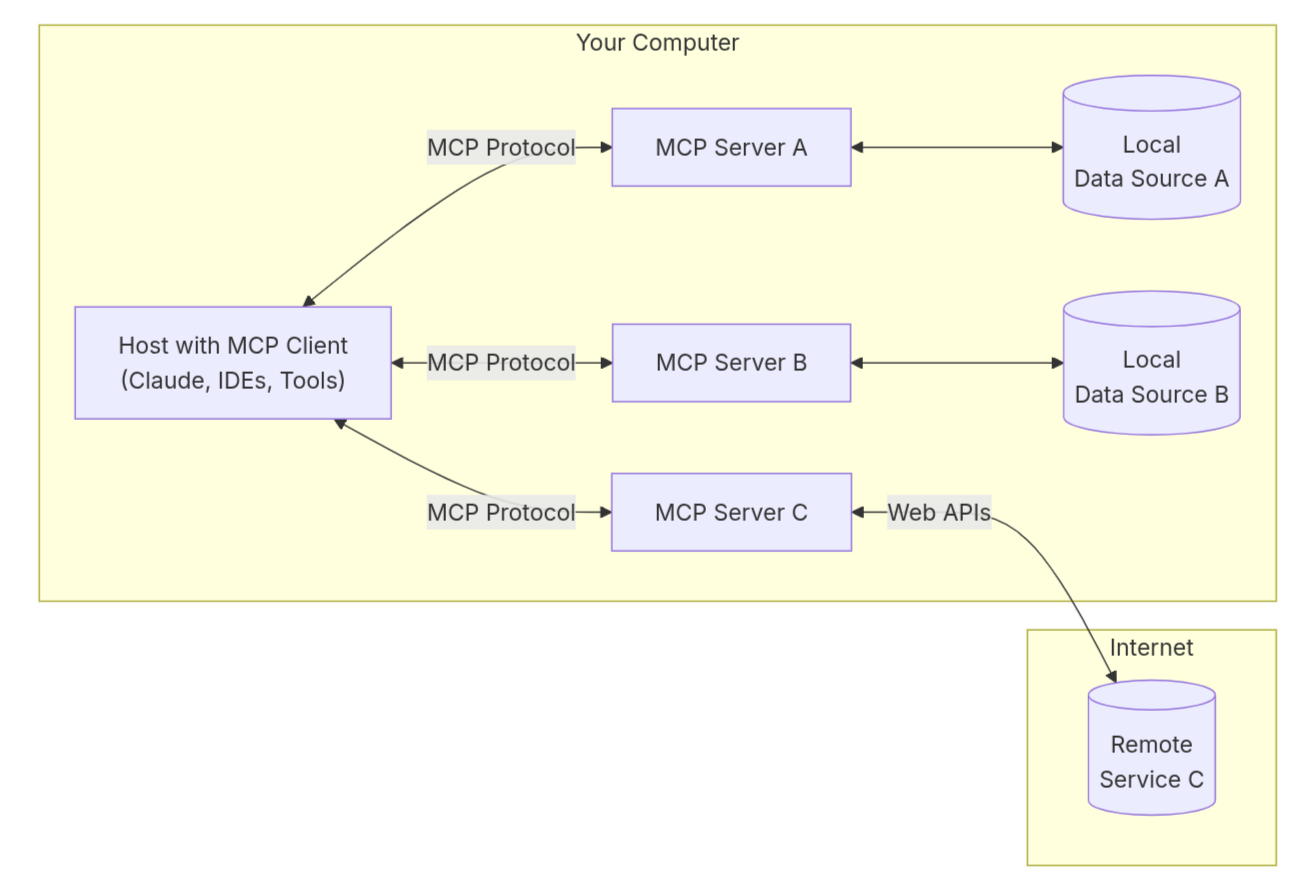
在网页中连接操作系统
观察上面的流程,如果我们自己来启动服务/使用公开的网络服务
那完全可以在网页中使用 MCP Server 来连接操作系统,而不一定非要使用一个客户端软件来承接